Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
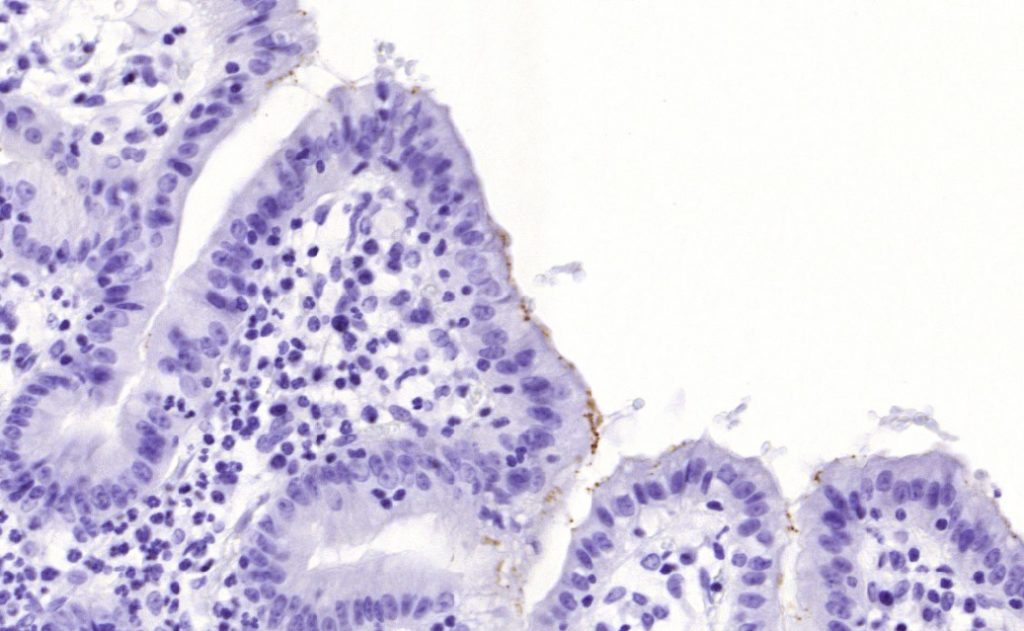
The spiral shaped bacteriumHelicobacter pyloriis strongly associated with inflammation of the stomach and is also implicated in the development of gastric malignancy.H. pyloriis known to cause peptic ulcers and chronic gastritis in human. It is associated with duodenal ulcers and may be involved in development of adenocarcinoma and low-grade lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue in the stomach.This antibody stains the individual H. pylori bacterium when it presents on the surface of the epithelium or in the cytoplasm of the epithelial cells in biopsy tissue sections from the antrum and body of the stomach.
Availability:
| Catalog No. | Contents | Volume |
| ILM7225-C01 | Helicobacter | 0,1 ml concentrate |
| ILM7225-C05 | Helicobacter | 0,5 ml concentrate |
| ILM7225-C1 | Helicobacter | 1,0 ml concentrate |
Intended use: For Research Use Only
Reactivity: Human, others not known
Clone: HPLY/7225
Species of origin: Mouse
Isotype: IgG1, Kappa
Immunogen: Recombinant Helicobacter pylori Catalase protein fragment (around aa323-445) (Exact sequence is proprietary)
Control Tissue: H. Pylori infected stomach tissue
Staining: Cytoplasmatic
Presentation: Bioreactor Concentrate with 0.05% Azide
Application and suggested dilutions:
Pre-treatment: Heat induced epitope retrieval in 10 mM citrate buffer pH6.0 for 20 minutes is required for IHC staining on formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded tissue sections.
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded tissue section (dilution up to 1:100-1:200)
The optimal dilution for a specific application should be determined by the investigator.
Note: Dilution of the antibody in 10% normal goat serum followed by a Goat anti-Mouse secondary antibody-based detection is recommended.
Storage & Stability: Store at 2-8 °C. Do not use after expiration date printed on the vial.
Reference:
- N.F. Azevedo, N. Guimareas, C. Figueiredo, C.W. Keevil, M.J. Viera, A new model for the transmission of Helicobacter pylori; role of environmental reservoirs as gene pools to increase strain diversity. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 33 (2007) 157-169.
- M. Czesnikiewicz-Guzik, W. Bielanski, T.J. Guzik, B. Loster, S.J. Konturek, Helicobacter pylori in the oral cavity and its implication for gastric infections, periodontal health, immunology and dyspepsia, J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 56 (Suppl. 6) (2005) 77-89.